This series contains 14 animated historical maps. For a preview, please consult the map below:
▶ Independence for India and Pakistan
SubscribeDecolonization after 1945
The reasons why decolonization took place are many and complex, varying widely from one country to another. Three key elements played a major role in the process: colonized peoples' thirst for independence, the Second World War which demonstrated that colonial powers were no longer invulnerable, and a new focus on anti-colonialism in international arenas such as the United Nations.
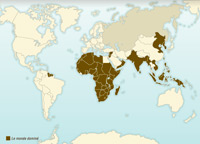
Colonial world dominance in 1939
Video extract
Before the Second World War broke out, a large proportion of the world's population was living under the sovereignty of a colonial power, for the most part European. European domination in Africa was particularly impressive.
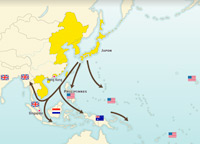
World War II undermines the colonial system
Video extract
Myths such as the invulnerability of colonial powers and white supremacy were seriously challenged by the outbreak of the Second World War.
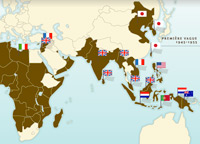
Accelerated decolonization after 1945
Video extract
Following the Second World War, the colonial system was subject to growing unrest, and many countries quickly acquired their independence.
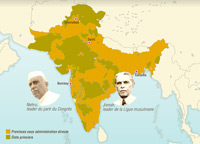
Independence for India and Pakistan
Complete video
Clement Attlee, the Labour Prime Minister who replaced Winston Churchill in July 1945, soon realised that independence for India was inevitable, but disagreements among the Indian politicians made the negotiations very difficult.
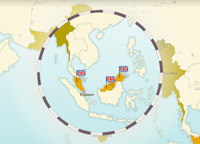
Independence for Burma, Ceylon and Malaysia
Video extract
Burma and Ceylon (later Sri Lanka) obtained their independence soon after India but in Malaysia the situation was more complex.
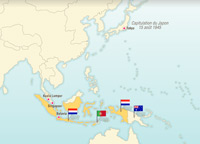
Independence for the Indonesian Archipelago
Video extract
A direct consequence of Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies during the Second World War was the emergence of Indonesian nationalism. Nevertheless, at the end of the war, the Netherlands was opposed to their independence.
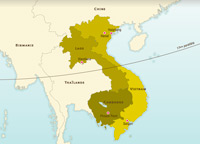
Independence for Indochina
Video extract
The Communist Party led by Ho Chi Minh took advantage of the Japanese occupation of Indochina during the Second World War to launch the Viet Minh Independence Movement. The failure to create an Indochinese federation in 1946 as part of the French Union led to a long war of independence.
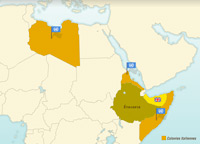
Independence for Italy’s African colonies
Video extract
Independence for Italy’s African colonies (Ethiopia, Libya, Eritrea, Somalia) came as a direct consequence of Italy’s downfall during the Second World War.
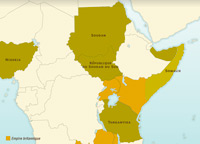
Decolonization of the United Kingdom’s territories in Africa
Video extract
In Africa, the United Kingdom launched the process of decolonization in the early 1950s. Some countries achieved independence peacefully. Others, however, became embroiled in inter-community rivalries or faced opposition from the British colonial settlers.
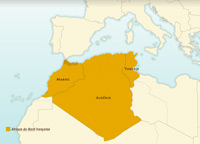
Decolonization of North Africa by France
Video extract
French North Africa covered three territories: the Protectorates of Morocco in the west and Tunisia in the East, with Algeria in the centre. Algeria was considered by France to be an extension of its national territory and only obtained its independence after a long, drawn-out conflict which lasted 8 years.
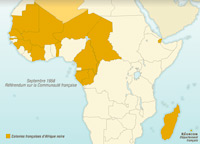
Decolonization of French black Africa
Video extract
Independence in Africa was introduced in phases. Most of the French colonies in Black Africa became independent in 1960.
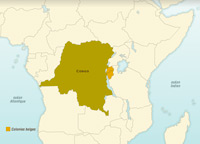
Independence for Belgium’s African colonies
Video extract
The immense Belgian Congo was one of the richest colonies in Africa. After bloody riots in 1959, the Belgian Government quickly yielded to demands for independence in 1960.
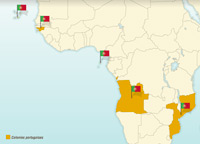
Independence for Portugal’s African colonies
Video extract
Portuguese colonies in Africa gained their independence only after the “Carnation Revolution” which took place in Lisbon in April 1974.
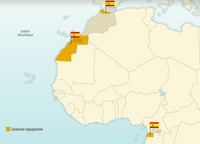
Independence for Spain’s African territories
Video extract
North of Morocco, Spanish Guinea and Western Sahara gained their independence from Spain between 1956 and 1975.