This series contains 16 animated historical maps. For a preview, please consult the maps below:
▶ The evolving Greek world
▶ Athenian Democracy
Subscribe
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece played a major role in the development of Western civilization and laid down the foundations of democracy.
This series evokes Crete and Mycenae, colonization and Greek cities, the wars between Persia and the Athenian empire, Sparta and the Peloponnesian war, Alexander's conquests and the Hellenistic kingdoms.
In an evolving geographic area, Ancient Greece's two thousand years of history have inspired our imagination.
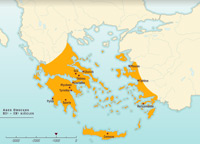
The evolving Greek world
Complete video
The Greek world was an ever-changing geographical reality throughout three million years before Christ. Greek civilization started with the first settlements in the Cyclades and Crete and later on both sides of the Aegean Sea, colonization then evolved along the Mediterranean coast and around the Black Sea before culminating in the immense empire created by Alexander the Great. Divided by internal dissension, the Hellenistic world was gradually absorbed into the Roman Empire, though Greek culture continued to develop throughout the Mediterranean Basin.
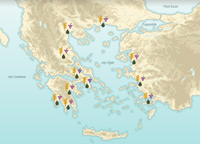
Geography of Greece
Video extract
Greece is dominated by two main geographical features: sea and mountains. The mountain ranges sweep down from the centre to the shore, isolating the coastal plains: Thrace, Macedonia, Thessaly, Boeotia, Attica, Laconia, and Messenia.
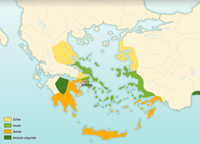
Migration and languages
Video extract
The end of the 3rd millennium BC was marked by several waves of migration over a long period: Ionians, Aeolians, Achaeans, Dorians. These migrations led to the emergence of various Greek dialects in different geographical regions around the Aegean Sea.
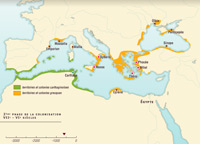
Colonization
Video extract
In the 8th century, and over the next two centuries, the Greeks were well established on both sides of the Aegean Sea and continued to expand their world through colonization. For the Greeks, this meant leaving their own cities to found others in Magna Graecia, on the Mediterranean coast and the Black Sea (Euxeinos Pontos, Hellespont).
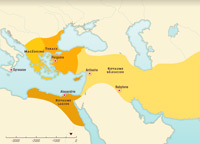
The Hellenistic kingdoms
Video extract
When he died at the age of 33, Alexander had no direct heirs. This situation led to his empire being divided between his generals, known as the ‘diadochi’. There followed forty years of partitions and wars, during which the diadochi squabbled over Alexander’s empire and created a number of independent kingdoms.
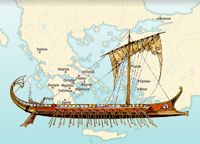
The Greeks and War
Video extract
Wars were a common phenomenon in Ancient Greece. These were sometimes wars against external enemies, but mostly they involved conflicts between neighbouring cities. The army was made up of infantrymen, the hoplites, who marched in phalanxes, that is, in a tight formation of 8 rows.
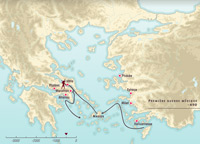
The Greco-Persian Wars
Video extract
The wars between the Greeks and the Persians took place in the early 5th century BC. They began when Greek cities in Asia Minor rebelled against their Persian overlords. Victories in the Battles of Marathon and of Salamina gave Athens additional prestige and allowed them to dominate the areas around the Aegean Sea.
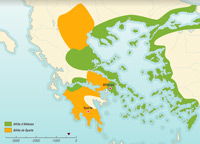
The Peloponnesian War
Video extract
The Peloponnesian War involved the two largest power centres in Greece: Athens backed by its empire and Sparta with its allies in the Peloponnesian League. This conflict was important for many reasons: its unprecedented length, the number of cities involved in the fighting and the vast number of battle sites.
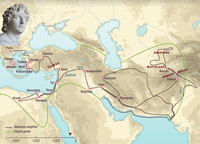
The conquests of Alexander the Great
Video extract
Alexander the Great is one of the most famous men of the Ancient world. He defeated Darius at Issus and Gaugamela, and took over the entire Persian Empire which stretched from the Mediterranean to India. The wedding at Susa demonstrated Alexander’s desire to bind together the Macedonians, Greeks and Asians into a single people.
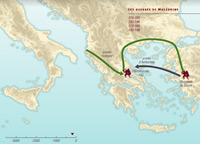
Conflicts with Rome
Video extract
During the 3rd century BC, Southern Italy and Sicily became part of the Roman State, and some Greek cities decided to form alliances with their powerful new neighbour. But it was the “Macedonian Wars” that gave Rome a foothold in the region. The Romans made alliances with the small kingdoms that had been created and were now fighting against the descendants of the diadoci.

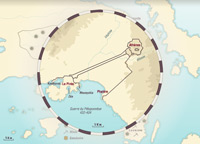
Mycenae
Video extract
Around 1600 BC, the Achaeans settled in the Peloponnese where they founded a number of cities including Pylos and Mycenae. Archaeological excavations carried out at Mycenae, and the many Greek legends that refer to the city, have led to this civilization being known as the “Mycenaean world”.
A Greek city-state: Athens
Video extract
A Greek city, or polis, was an independent city-state that shared the same language and values with other Greek cities. It was made up of a group of free men who could participate in government: the citizens. The city of Athens is a typical example of a classic city-state.
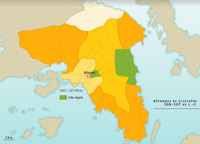
Athenian Democracy
Complete video
Between 508-507 BC, the Cleisthene reforms established the framework for democracy, thanks to the creation of an egalitarian civic space. These reforms were intended to create new bonds between citizens living in the various regions in Attica as well as to break down traditional clan and family relationships. During the following decades, victories in the battles of Marathon and Salamina over the Persians reinforced the prestige of Athenian democracy.
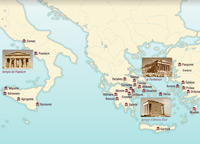
The temples
Video extract
Once the Greeks began to make sculptures of their gods in human form, the temple which housed the statue(s) became an essential part of any sanctuary. Architecture in Ancient Greece can be characterized as one of three types: the Doric, Ionian and Corinthian orders.
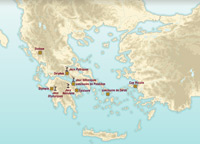
The Pan-Hellenic sanctuaries
Video extract
Religion was an integral part of life for the Greeks. Some sanctuaries, known as Pan-Hellenic sanctuaries, attracted large regional and international gatherings and played an important role in the emergence of Greek consciousness, known as Hellenism. These sanctuaries (Delphi, Dodona, Olympia, Delos) were located close to major routes and crossroads.
Alexandria: A Hellenistic City
Video extract
In order to revive trading opportunities in the Eastern Mediterranean, after his conquest of Egypt Alexander the Great ordered that the city of Alexandria be built. At the time, it was the only Egyptian port on the Mediterranean coast. Aside from being an important centre for trading and power, Alexandria remained for many centuries the intellectual capital of the Mediterranean as well.