This series contains 15 animated historical maps. For a preview, please consult the maps below:
▶ The War goes Global, June 1941 – end 1942
▶ The Final Solution (The Holocaust, The Shoah)
SubscribeThe second World War, 1939-1945
Hitler's invasion of Poland in September 1939 led to the outbreak of the Second World War.
During the early stages, the conflict was confined mainly to Europe, but later extended to the rest of the world following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor which led to the United States also entering the war.
The "total war" mobilized the economic and industrial resources of all belligerents and caused the death of some 50 million people, most of whom were civilians.
The war ended with the fall of Berlin to the Red Army in May 1945 and the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in early August 1945.
Moving towards War
Video extract
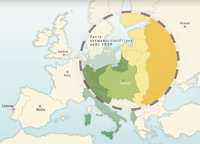
In Europe: Mussolini and Hitler take power, there is the remilitarisation of the Rhineland in 1936, Anschluss in 1938, Munich Conference in 1938, German-Soviet Non-Aggression Treaty of 1939. In Asia: Japanese Protectorat in Manchuria 1931, Japanese campaign against China 1937.
War in Europe 1939-1941
Video extract
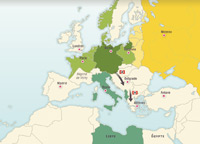
Invasion of Poland, September 1939; the Phoney War, Narvik, Invasion of the Netherlands, Belgium and France, Battle of Britain, the Submarine War, Occupation of Yugoslavia and Greece. Afrika Korps in Libya, Tobruk.
The Blitzkrieg
Video extract
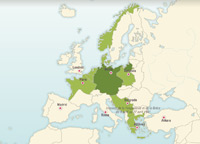
Blitzkrieg: a series of joint air and tank attacks. The German Army provokes successful lightning attacks during the early phases of the war.
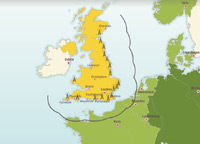
The Battle of Britain July- November 1940
Video extract
Operation Sealion, the various phases of the Battle of Britain, the Blitz begins 7 September, major air raids on London and other English cities.
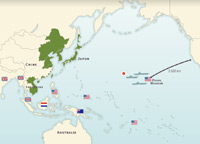
The War goes Global, June 1941 – end 1942
Complete video
In Europe: Operation Barbarossa, June 1941. Siege of Leningrad, Germany and Italy declare war on the United States, Germany’s Russian campaign in 1942, Stalingrad. In Asia: Pearl Harbor 7 December 1941, Japanese campaign in Southeast Asia. Air-sea battles: Coral Sea, Midway, US landing at Guadalcanal.
German Europe in 1942
Video extract
In 1942, most of Europe is dominated by Germany. The Reich’s objective: to use mineral resources found in occupied territories for its war industry. Germany uses brutal repression and massacres in occupied countries. The decree “Nacht und Nebel”, Wansee conference, Resistance movements.
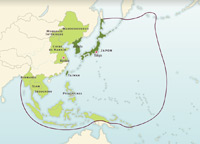
Asia: Japanese Power in 1942
Video extract
In 1942, Japanese control of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands; Japanese government’s conquests in search of resources to finance the war effort; sphere of co-prosperity.
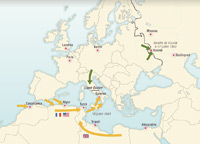
The Turning Point, autumn 1942 to end 1943
Video extract
On 8 November 1942, a second Allied front in North Africa. Operation Torch On 2 February 1943, surrender of German 6th Army in Stalingrad. On 9 February, end of Japanese resistance at Guadalcanal. Battle of Kursk July 1943. Allied landings in Sicily and Italy. November Stalin, Churchill and Roosevelt meet in Tehran.
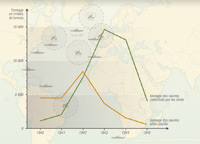
The Battle of the Atlantic
Video extract
The United Kingdom's economy is dependent on imported goods; The Battle of the Atlantic holds a major stake in the Second World War.
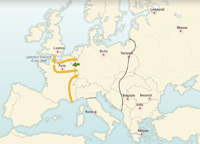
Allied Victory 1944-1945
Video extract
End 1943, the Axis powers lose ground on three major fronts: USSR, the Mediterranean and Asia-Pacific. Allies concentrate on Germany before seeking victory over Japan. Normandy landings, June 1944, landings in Provence August 1944. Surrender by Germany, 8 May 1945. Official Japanese surrender signed on 2 September 1945.
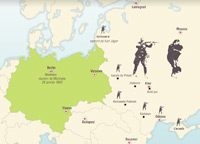
The Final Solution (The Holocaust, The Shoah)
Complete video
Radical anti-Semitism promoted by Hitler and his regime. The Polish ghettos, Massacres by the Einsatzgruppen; the extermination camps: Sobibor, Majdanek, Belzec, Chelmno and Auschwitz-Birkenau; the Wansee Conference; between 5 and 6 million European Jews killed between September 1939 and May 1945.
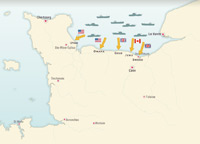
The D-Day Landings and the Battle of Normandy
Video extract
Operation Overlord, D-Day 6 June 1944; Allied landings on Omaha, Utah, Gold, Sword and Juno beaches; capture of Cherbourg, 26 June; 24 July, several thousand airplanes launch a huge carpet bombing attack on the Normandy countryside. General Patton’s American tank divisions reach Avranches on 30 July.
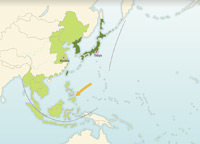
Military Operations in Asia 1944-1945
Video extract
Japanese campaigns in Burma and China 1944; Reconquest of the Mariana Islands and the Philippines; Capture of Iwo Jima and Okinawa in March and June 1945; Atomic bombs on the city of Hiroshima on 6 August 1945 and on Nagasaki three days later; Japanese surrender, 2 September 1945.
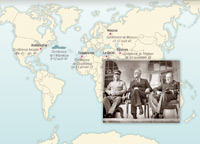
Major International Conferences
Video extract
Throughout the war, the Axis military powers did not coordinate their campaigns. The Allies held regular international conferences during which they discussed major strategies and plans for the post-war period. Conferences in Casablanca, Tehran, Yalta, Potsdam.
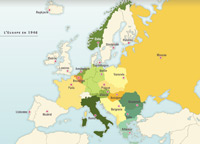
Allied Decisions after the War
Video extract
Creation of the UN, Nuremberg and Tokyo trials, occupation of Germany, major territorial decisions in Europe and Asia.